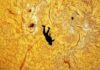
The Curiosity rover has uncovered a significant anomaly on Mars: a deposit of pure elemental sulfur in the Gediz Vallis Channel. This unexpected find, revealed after the rover accidentally crushed a rock in May of last year, marks the first confirmed instance of naturally occurring elemental sulfur on the red planet.
The Discovery and Its Significance
Sulfates, compounds containing sulfur, are common on Mars, telling scientists about past water activity and weathering patterns. However, pure sulfur formation requires very specific conditions not previously understood to exist in this region of Mars. The discovery suggests either previously unknown geological processes or a missing piece in our understanding of the planet’s history.
According to Ashwin Vasavada of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, “Finding a field of stones made of pure sulfur is like finding an oasis in the desert… It shouldn’t be there, so now we have to explain it.” The presence of similar-looking rocks in the area suggests that elemental sulfur may be more widespread than initially assumed.
What Does This Mean?
The presence of sulfur, while not direct evidence of life, is notable because it is an essential element for all known life forms. It is used in the creation of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. This discovery adds to the growing list of resources on Mars that could potentially support microbial life, though no definitive signs have yet been found.
The question now is how this sulfur formed. The geological history of Mars remains incomplete, and this finding indicates a gap in our knowledge. Scientists will need to refine their models of Martian evolution to explain this unexpected presence.
Ongoing Exploration and Future Research
Curiosity continues to traverse the Gediz Vallis Channel, gathering more data on the surrounding geology. Meanwhile, the Perseverance rover is also actively exploring the Martian surface, recently achieving a record-breaking drive of 411 meters in a single day.
The continued exploration of Mars is driven by the human spirit of discovery, and these findings reinforce the importance of robotic missions in unraveling the mysteries of our solar system.
The discovery of elemental sulfur on Mars is a reminder that planetary science is full of surprises, and that even well-studied regions can still hold unexpected secrets. Further research will be crucial to understanding the origins of this sulfur and its implications for Martian geology and habitability.